MinieyeDDS
注意
本文档仅适用于 v1.18.0(不包含) 之前版本
📦 发布文件
- libdds.so
- libdds_api.so
- libnanomsg.so
- dds_api.h
- dds_capi.h
- dds_common.h
- config.json
原理介绍
MinieyeDDS 是一个基于 Rust 构建的消息中间件组件,它提供了包括 C、C++、Python、Rust 等接口,拥有良好的跨平台特性。
通信协议
MinieyeDDS 底层是通过共享内存进行通信的,同时引入了 Nanomsg 作为实现数据的发布订阅功能的组件。
消息传输
一个比较典型的传输场景是这样的:
- 启动生产者,初始化 MinieyeDDS,创建共享内存和 nanomsg 发布者
- 启动消费者,初始化 MinieyeDDS,尝试连接到共享内存、创建 nanomsg 订阅者并且订阅相关 topic
- 生产者发送数据,将数据写入共享内存,然后通过 nanomsg 发布消息
- 消费者通过 nanomsg 收到消息,访问共享内存以获取相关数据
架构设计
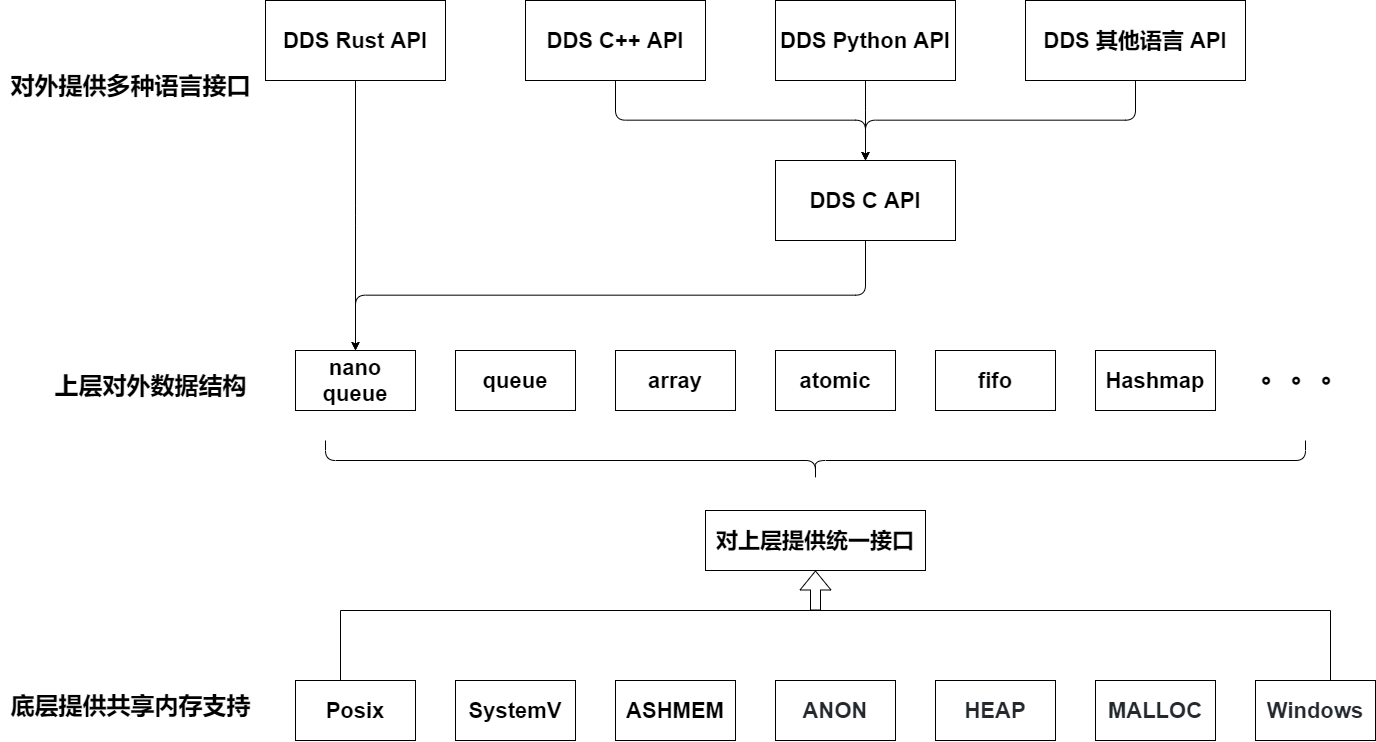
如下图所示,MinieyeDDS 在底层提供对不同的共享内存类型的封装,对上层提供统一的接口。上层可以基于共享内存的统一接口实现各种不同的数据结构。目前常见的数据结构有队列,数组,原子变量等等。再向上一层,是 MinieyeDDS 为了方便使用者快速入门而提供的一套接口,也可以称为 DDS API。DDS API 提供不同语言的封装。DDS API 目前是基于 nanomsg queue 这个数据结构实现的。
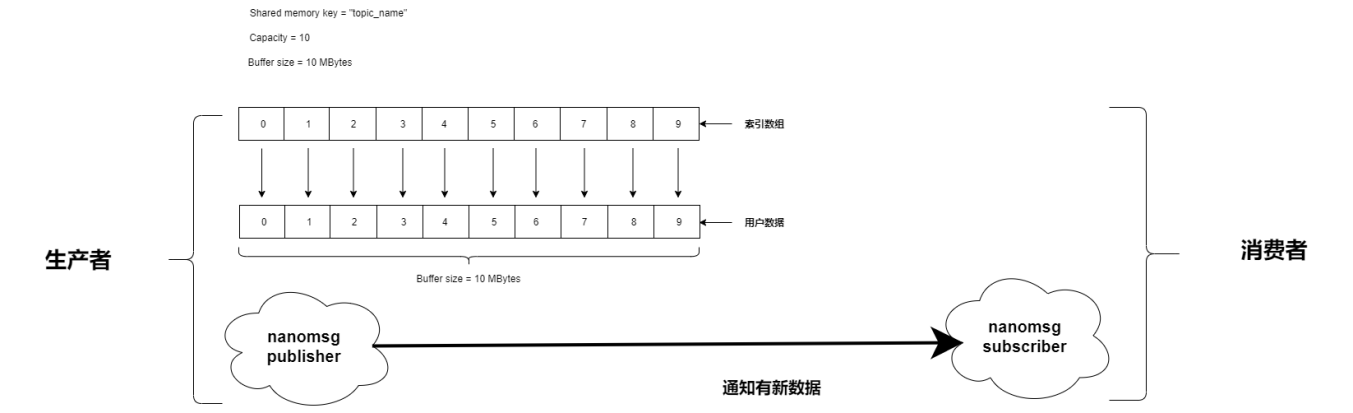
如下图所示,生产者会创建一个共享内存,同时会创建一个 nanomsg 的发布者。消费者会连接到共享内存上,同时创建一个 nanomsg 的订阅者。
MinieyeDDS 的共享内存分为两个部分:
- 索引数组:存储每个数据的唯一标识、数据的下标和数据的长度等信息
- 数据数组:存储用户写入的具体数据
开发指南
引入 MinieyeDDS
使用 C++ 开发时,需要引入以下两个头文件
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"同理,使用 C 开发时,需要引入以下两个头文件
#include "dds_capi.h"
#include "dds_common.h"除了引入上述的头文件以外,还需要引入共享库 libdds.so、libdds_api.so 和 libnanomsg.so
服务端
与 Libflow 类似,每个服务端都需要由一个 Context 管理,并且在一个进程中,只能初始化一个 Context,额外的初始化可能会导致程序的崩溃。
启动一个 MinieyeDDS 服务端之前,我们需要为其添加一个配置文件,配置文件应为 JSON 格式:
// config.json
{
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
}有了配置文件以后,我们可以利用它实例化一个 MinieyeDDS 服务端程序:
using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 配置文件的路径
const std::string configPath = "/path/to/config.json";
// 通过配置文件实例化一个 Context 对象
Context ctx(configPath);
// 通过 Context 对象实例化一个 Writer 对象
// 第二个参数表示这个 writer 对象负责向话题 test 写入消息
Writer writer(&ctx, "test");也可以不额外使用 json 文件进行配置:
using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 直接写配置
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
// 实例化 ctx 对象,第一个参数是配置参数
// 第二个参数是一个占位符,表示直接从字符串读取配置
Context ctx(config, ContentHint());
Writer writer(&ctx, "test");拥有 minieye::DDS::Writer 对象以后,就可以向客户端写入消息了:
// 写线程,负责写入数据到客户端
void funcWriter(Writer* writer) {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
// 生产需要向客户端发送的消息
std::string payload = "Hello world " + std::to_string(i);
// 向 queue 写入数据
int ret = writer->Write(payload.c_str(), payload.size());
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("Write failed, ret = %d\n", ret);
}
std::cout << "Write data = " << payload << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
}客户端
与服务端相同,客户端也需要使用一个 Context 来管理:
/** config.json
{
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
} */
using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 配置文件的路径
const std::string configPath = "/path/to/config.json";
// 通过配置文件实例化一个 Context 对象
Context ctx(configPath);
// 通过 Context 对象实例化一个 Reader 对象
// 第二个参数表示这个 reader 对象负责向话题 test 写入消息
Reader reader(&ctx, "test");using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 直接写配置
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
// 实例化 ctx 对象,第一个参数是配置参数
// 第二个参数是一个占位符,表示直接从字符串读取配置
Context ctx(config, ContentHint());
Reader reader(&ctx, "test");请注意
因为服务端和客户端会连接到同一块共享内存,因此请确保服务端和客户端的配置文件相同
MinieyeDDS 客户端提供了两种方式来读取从服务端发送的消息:
// 使用回调之前,需要首先定义一个回调函数
void on_read_data(
const char* topic, // 主题
size_t index, // array 索引
void* ptr, // 接收到的数据地址
size_t size, // 接收到的数据长度
void* user // 用户自定义数据
) {
std::string content((char*)ptr, size);
std::cout << "package received, idx: "
<< index
<< ", frame size: "
<< size
<< ", content: "
<< content
<< std::endl;
}
// 使用回调函数还需要在 Context 初始化的时候说明
int main() {
// ...
Context ctx("config.json", true);
// 从字符串读取配置文件的情况
// Context ctx(config, ContentHint(), true);
Reader reader(&ctx, topic, on_read_data);
// ...
return 0;
}void ThreadReader(Reader* reader) {
while(true) {
char acBuf[1024] = {0};
size_t numLength = sizeof(acBuf);
size_t id = 0;
size_t index = 0;
int ret = reader->ReadNotify(acBuf, &numLength, &id, &index);
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("ReadNotify failed, iRet = %d\n", ret);
continue;
}
// 获取 topic array 的容量
size_t shm_capacity = 0;
reader->Capacity(&shm_capacity);
printf("ReadNotify %zu [id:%zu, index:%zu] data = %s\n", shm_capacity, id, index, acBuf);
}
}配置文件
MinieyeDDS 的配置文件是 JSON 格式的,其中有三个字段比较重要:
log_level
表示需要启用的日志等级,可选:
1: Error(推荐), 2: Warn, 3: Info, 4: Debug, 5: Trace, 0: close
topics
表示需要申请的共享内存,一个 topic 对应一个共享内存,topics 是一个数组,由 n 个如下结构的元素构成:
{
"topic": "topic_name", // topic 名称,需要确保唯一
"dds_mode": "shm", // dds 模式,默认 shm
"buff_num": 200, // node 的数量
"elem_max_size": 1000, // 每个 node 的最大体积(bytes)
// 注意:buff_num x elem_max_size
// 并不等于实际使用共享内存大小
"url": "tcp://127.0.0.1:8088", // 通信连接地址 nanomsg url (非必须)
}示例代码
Pub-Sub
在 Pub-Sub 中:
- 我们创建一个服务端,服务端会尝试创建话题 test 并且 Publish 到所有订阅了该话题的客户端
- 我们创建一个客户端,这个客户端会订阅话题 test,并且显示所有从服务端接收到的话题
配置文件如下:
// config.json
{
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
}代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 写线程,负责写入数据到客户端
void ThreadWriter(Writer* writer) {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
std::string payload = "Hello world " + std::to_string(i);
// 向 queue 写入数据
int ret = writer->Write(payload.c_str(), payload.size());
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("Write failed, ret = %d\n", ret);
}
std::cout << "Write data = " << payload << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
}
int main() {
const std::string configPath = "/path/to/config.json";
Context ctx(configPath);
Writer writer(&ctx, "test");
ThreadWriter(&writer);
return 0;
}#include <signal.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
void on_read_data(const char* topic, size_t index, void* ptr, size_t size, void* user) {
std::string content((char*)ptr, size);
std::cout << "package received, idx: "
<< index
<< ", frame size: "
<< size
<< ", content: "
<< content
<< std::endl;
}
int main() {
const std::string configPath = "/path/to/config.json";
Context ctx(configPath, true);
Reader reader(&ctx, topic, on_read_data);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(30));
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
// 读线程,负责从 reader 中读取消息
void ThreadReader(Reader* reader) {
while(true) {
char acBuf[1024] = {0};
size_t numLength = sizeof(acBuf);
size_t id = 0;
size_t index = 0;
// 从 queue 中读取消息
int ret = reader->ReadNotify(acBuf, &numLength, &id, &index);
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("ReadNotify failed, iRet = %d\n", ret);
continue;
}
// 获取 topic array 的容量
size_t shm_capacity = 0;
reader->Capacity(&shm_capacity);
printf("ReadNotify %zu [id:%zu, index:%zu] data = %s\n", shm_capacity, id, index, acBuf);
}
}
int main() {
const std::string configPath = "/path/to/config.json";
Context ctx(configPath);
Reader reader(&ctx, "test");
ThreadReader(&reader);
return 0;
}当然,我们也可以从字符串读取配置
#include <iostream>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
// 写线程,负责写入数据到客户端
void ThreadWriter(Writer* writer) {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
std::string payload = "Hello world " + std::to_string(i);
// 向 queue 写入数据
int ret = writer->Write(payload.c_str(), payload.size());
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("Write failed, ret = %d\n", ret);
}
std::cout << "Write data = " << payload << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
}
int main() {
Context ctx(config, ContentHint());
Writer writer(&ctx, "test");
ThreadWriter(&writer);
return 0;
}#include <signal.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
void on_read_data(const char* topic, size_t index, void* ptr, size_t size, void* user) {
std::string content((char*)ptr, size);
std::cout << "package received, idx: "
<< index
<< ", frame size: "
<< size
<< ", content: "
<< content
<< std::endl;
}
int main() {
Context ctx(config, ContentHint(), true);
Reader reader(&ctx, topic, on_read_data);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(30));
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
// 读线程,负责从 reader 中读取消息
void ThreadReader(Reader* reader) {
while(true) {
char acBuf[1024] = {0};
size_t numLength = sizeof(acBuf);
size_t id = 0;
size_t index = 0;
// 从 queue 中读取消息
int ret = reader->ReadNotify(acBuf, &numLength, &id, &index);
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("ReadNotify failed, iRet = %d\n", ret);
continue;
}
// 获取 topic array 的容量
size_t shm_capacity = 0;
reader->Capacity(&shm_capacity);
printf("ReadNotify %zu [id:%zu, index:%zu] data = %s\n", shm_capacity, id, index, acBuf);
}
}
int main() {
Context ctx(config, ContentHint());
Reader reader(&ctx, "test");
ThreadReader(&reader);
return 0;
}关闭 topic
在《关闭 topic》中:
- 我们创建一个服务端,这个服务端会尝试创建话题 test,并且 Publish 到所有订阅了该话题的客户端,在第 10s 时,服务端会关闭这个 topic,并且在第 20s 时重新打开这个话题
- 我们创建一个客户端,这个客户端会尝试订阅话题 test,并且显示所有从服务端接收到的消息,在第 30s 时,客户端会尝试关闭回调功能,意味着尽管客户端接收到这个消息了,它也不会做出相应的回调处理,在第 40s 时,客户端会重新打开回调功能
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
void ThreadWriter(Writer* writer) {
int idx = 0;
while (true) {
char acData[1024] = {0};
sprintf(acData, "shared memory, hello dds, %d", idx++);
// 向 queue 写入数据
int ret = writer->Write(acData, strlen(acData) + 1);
if (ret != DDSSuccess) {
printf("Write failed, iRet = %d\n", ret);
}
printf("Write data = %s\n", acData);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
}
int main() {
// 先把之前旧的从系统中删除。
// rshm_unlink_multi_posix(topic, 2);
// rshm_unlink_multi_svpic(topic, 2);
Context ctx(config, ContentHint());
Writer writer(&ctx, "test");
std::thread t1(ThreadWriter, &writer);
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) {
if (i == 10) {
writer.disable();
std::cout << "disable" << std::endl;
}
if (i == 20) {
writer.enable();
std::cout << "enable" << std::endl;
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
}
t1.join();
return 0;
}#include <signal.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include "dds_api.h"
#include "dds_common.h"
using namespace minieye::DDS;
const std::string config = R"({
"log_level": 1,
"topics": [{
"topic": "test",
"dds_mode": "shm",
"buff_num": 200,
"elem_max_size": 10000
}]
})";
void onData(const char* topic, size_t index, void* ptr, size_t size, void* user) {
printf("[topic: %s] array[%lu] = %d\n", topic, index, *(int*)ptr);
}
int main() {
// 先把之前旧的从系统中删除。
// rshm_unlink_multi_posix(topic, 2);
Context ctx(config,ContentHint(), true);
Reader reader(&ctx, "test", onData);
for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) {
if (i == 30) {
reader.disable();
std::cout << "disable" << std::endl;
}
if (i == 40) {
reader.enable();
std::cout << "enable" << std::endl;
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
}
return 0;
}